Hard money main three categories
Hard money loan programs are divided roughly into three main categories: Hard-hard money (HH), Soft-hard money (SH), and None-QM (NQ). Although the common denominator of all hard money loans is the reliance upon property equity, the SH and NQ lenders take credit and the ability to repay into consideration when underwriting the loan.
Hard-hard money (HH)
Historically hard money lending was strictly about the equity left in the property after the loan was made. Many lenders are still lending based only on the loan low loan to value, up to 55% -65% regardless of credit or income, and provided that the property is a none-owner occupied or the purpose of the loan is strictly for business.
Soft-hard money (SH)
Until the advent of the internet, the HH (hard-hard money loans) were the only hard money available. When private lenders could factor in the borrower's credit and ability to repay, they raise the LTV to 70% and 75% with soft-hard money loans - SH. The difference between the hard-hard money and the soft-hard money is that on the latter, the lenders will extend higher loan amounts, higher LTV, or lower Rat& Terms to borrowers who can demonstrate the ability to repay and/or have a good credit history.
None-Qm, Subprime (NQ)
The Non-Qm lenders, aka subprime, Alt-A, or portfolio lenders, can underwrite loans with bank statements or use the borrower assets instead of tax returns. Non-QM lenders don't characterize themselves as hard money because of their low-interest rates and long-term loan programs.
Non-Qm could be considered a stand-alone category (not entirely hard money lending yet not bank lending).
However, because some Non-QM loan programs don't require income verification, we included them in the hard money lending category. Borrowers searching Lendersa® for hard money lenders may be pleasantly surprised to find out that they qualify for better Rates & Terms offered by Non-Qm lenders.
Hard money current rates:
Lendersa® compiles hard money loan rates from thousands of hard money lenders nationwide. As of Sunday 12/21/2025 12:00:00 AM current average hard money loan rates
|
Rate |
Point |
Term |
| Non-QM |
4.38% |
1.13 |
30 years |
| Soft-Hard |
8.91% |
1.60 |
1-30 years |
| Hard-Hard |
9.96% |
2.03 |
1-5 years |
Loans rates, terms, speed of funding, and loan approval conditions widely vary among private money lenders, compare, apply, optimize, and start saving today. Find local rates in your area:
What hard money loan are you qualified to get?
It all depends on Property type, Property condition, Location, Credit, Income, Property value, LTV, and verifications
What loan do you desire to get?
The Loan Amount, rate and terms, and the speed of funding affect the Rate & Terms
Use Lendersa® hard money loan calculator to get pre-approved in seconds and find the most optimum loan program that fits your needs.
Avoid costly mistakes when looking for a hard money loan. See Hard money secrets
Hard money lenders near me
|
Hard Money Loans(Subtypes) |
Underwriting priorities |
Source of funds |
Rate |
Duration |
Funding time |
Max LTV |
| HH |
Hard- hard money loans |
Mainly equity |
Private Investors |
7%-18% |
6-60 Mts |
3-15 days |
65% |
| SH |
Soft, hard money loans |
Equity credit and other factors |
Private Investors |
5%-12% |
12-60 Mts |
7-30 days |
75%
(Fix n' flip & blanket loan to 100%)
|
| NQ |
Non-QM loans Subprime loans Alt-A |
Credit equity and other factors |
Capital Portfolio |
3.00-9.5% |
10-40 Years |
20-60 days |
90% |
How difficult is it to get a Hard money loan?
In general, when the LTV is under 60%, all three types of hard money loans are available. Portfolio loans have the best rate & terms but take longer to fund. Non-Qm lenders take into consideration credit, and income can lend up 80% or 90% LTV. Fix N' Flip loans is a branch of hard money loans it takes into account the borrower's experience and can go up to 100% LTV or more.
The table below shows how the 3 categories of hard money lending apply to credit and Loan to Value
| FICO |
80% or more |
75% LTV |
70% LTV |
65% LTV |
60% LTV |
55% LTV |
50% LTV or less |
| 500 |
Not Available |
Not Available |
Not Available |
SH |
HH, SH |
HH, SH |
HH, SH |
| 550 |
Not Available |
Not Available |
Not Available |
SH |
HH, SH |
HH, SH |
HH, SH |
| 600 |
Not Available |
Not Available |
SH |
HH, SH |
HH, SH |
HH, SH |
HH, SH |
| 640 |
Not Available |
SH, NQ |
SH, NQ |
HH, SH, NQ |
HH, SH, NQ |
HH, SH, NQ |
HH, SH, NQ |
| 680 |
NQ |
SH, NQ |
SH, NQ |
HH, SH, NQ |
HH, SH, NQ |
HH, SH, NQ |
HH, SH, NQ |
| 700+ |
NQ |
SH, NQ |
SH, NQ |
HH, SH, NQ |
HH, SH, NQ |
HH, SH, NQ |
HH, SH, NQ |
What do you need to know about hard money?
There are books about Hard money, but they won't help you much because of market changes and new loan programs keep coming up, and private lenders are changing.
From the borrower's point of view, the names of subtypes' designation do not matter. What is essential are only the following issues:
1. How much money can I get?
2. What will it cost me? (Rate, fees, etc.)
3. How fast can I get it?
4. What do I need to have/show to close the loan?
Luckily for you, if you are using Lendersa® Super Loan Integrated Qualifier, all you need to do is enter the data, and the advance Lendersa® AI will get you all your options plus suggestions to improve your chances to reduce your rate and fees.
Hard money loans -types of properties
Non-Qm lenders only lend on residential properties, Hard-Hard money, and Soft-Hard money lenders lend on residential commercial and vacant land.
Lenders who lend on vacant land do not go above 35% LTV for undeveloped land and stay below 60 LTV on land already entitled subdivided and ready to be built.
Hard money loans in second 3rd or 4th position
About 20% of all HH and SH lenders often fund loans in the second position. The rates and points on second-position loans are normally higher by 2%-5%. When arranging loans in the 2nd, 3rd, or 4th position, the lender must consider the rate and terms of the liens which remain in a senior place.
The table below shows the availability of hard money funds for residential and commercial in the second position. The maximum LTV for the loans in the 3rd and 4th positions is lower than the LTV of the 2nd position loan because of the risk and complication involved with having several senior liens.
The table below shows how 2nd position loans are arranged based on Credit and LTV.
| FICO |
80% or more |
75% LTV |
70% LTV |
65% LTV |
60% LTV |
55% LTV |
50% LTV or less |
| 500 |
Not Available |
Not Available |
Not Available |
Not Available |
HH, SH |
HH, SH |
HH, SH |
| 550 |
Not Available |
Not Available |
Not Available |
Not Available |
HH, SH |
HH, SH |
HH, SH |
| 600 |
Not Available |
Not Available |
Not Available |
SH |
HH, SH |
HH, SH |
HH, SH |
| 640 |
Not Available |
SH |
SH |
SH |
HH, SH |
HH, SH |
HH, SH |
| 680 |
Not Available |
SH |
SH |
SH |
HH, SH |
HH, SH |
HH, SH |
| 700+ |
Not Available |
SH |
SH |
SH |
HH, SH |
HH, SH |
HH, SH |
100% hard money loan
There are two situations when it is possible to get a 100% LTV loan or even more. A. On Fix and Flip or construction loans, when the ARV is under 75% and the borrower have the rehab money, and B. when the borrowers pledge additional property with equity (Blanket loan)
Hard money Lenders
There are several names to those who arrange hard money loans. Some words have more than one definition; for example, a Hard money broker could also mean a private money lender. A hard money broker may transfer a loan file to a wholesale lender or fund the loan with his own money or his network of private investors.
Direct lenders
These hard money lenders have their source of funds and do not rely on other brokers or wholesale lenders. The direct lender sources of money are fund pools or private investors. The benefit of dealing with direct lenders is that they make their own decisions and quickly fund hard money loans. The disadvantage is that they have a narrow loan tolerance, and there are only certain types of loans in certain geographic locations that they could arrange.
How do hard money work
Direct lenders utilize two methods of funding hard money loans. Some lenders use both methods depending on the size and nature of the loan:
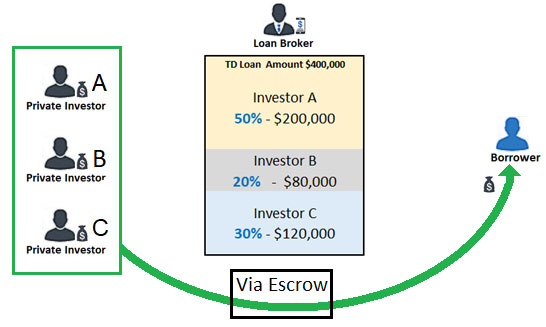
A. Old style -the lender package the loan and then contacts one or more private investors who inspect the package, and if accepted, they will fund the entire loan or portion of it through escrow. With this method, the money does not reach the lender's bank account but goes directly to the borrower via escrow/ title, who disperses it. Brokers who can fund the loan with their own money and sell it to investors after the borrower has already received it can get loans done faster than brokers who need to look for investors.
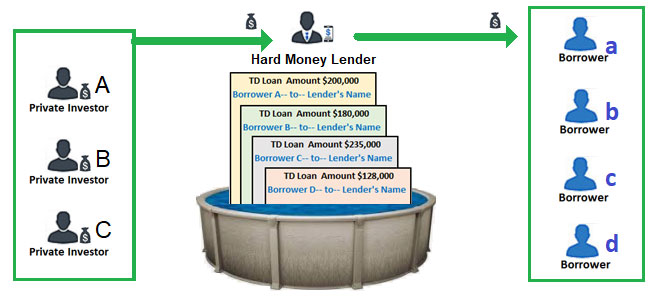
B. Mortgage pool- Private equity funds are aggregated from several investors and are used to fund hard money transactions at the discretion of the fund manager but are subject to rules and policy of the Mortgage pool. E.g., the loan size cannot exceed X amount, and the max LTV must be under a certain percentage and minimum XYZ credit score. The benefit of a mortgage pool is that the loan could be funded immediately without selling it to investors first. The disadvantage of the mortgage pool is that it is restricted by a guideline and must adhere to a specific parameter.
Wholesale hard money lenders
Wholesale lenders accept loans packages that hard money brokers originate. Brokers who procure borrowers but do not have private investors to fund the loan will transfer the loan package to the wholesale lender, who will fund it and pay the originator broker referral commission. Many wholesale lenders also have a retail division and therefore are also direct lenders. Hard money brokers who have access to private money can also act as wholesale lenders.
Private investors
Private investors are individuals with money who represent a family trust. Many Private investors are using their IRA account to invest in loans secured by real estate. Private investors do not interact directly with the borrower but only fund the loan after the hard money lender finishes the underwriting process. Find out how to become a private investor.
Hard money brokers
Brokers could act as direct lenders or loan originators who transfer the loan files to wholesale lenders. Brokers can also accept a loan from other brokers, and when they do, they are considered wholesale lenders. Brokers must be very familiar with sources of funds and regulations.
Direct lenders Vs. Brokers, which is better?
Many borrowers believe direct lenders are faster and less expensive than brokers, but it is not always true. Direct lenders are limited and many times restricted to do certain types of loans only. On the other hand, brokers are free to shop the loan to several direct lenders and could develop a loan solution when the direct lenders are stuck. Instead of deciding between direct lender and broker, we recommend pitching your loan to several brokers and several direct lenders to find the most optimum loan, which is not always the lowest rate. It could be a loan that can be funded in a few days or a loan without prepaying a penalty. Get more information on how to find hard money lenders.
Non-QM lenders
Major portfolio lenders who utilize wall street money, hedge funds, and or bundle many loans to sell on the secondary market. Non-Qm lenders are direct lenders; they could be wholesale lenders or retail lenders, and most of them have both retail and wholesale divisions.
Private money lenders
Is a general definition that could mean: Direct lenders, Bridge loan lenders, Private investors, equity lenders, assets base lenders, hard money brokers, or hard money lenders.


